一、从人外周血单核细胞诱导DCs(最常用方法)
1. 无菌条件下用密度梯度离心法从全血中获得人外周血单个核细胞(PBMCs)(如Ficoll-Hypaque)。
2. 磁珠分选法获得单核细胞:使用人单核细胞富集试剂盒(如EasySep(反选)或 CD14 MicroBeads(正选))富集获得单核细胞。富集得到的单核细胞可通过流式细胞术(CD3、CD14、CD19)检测其纯度。
3. 用培养基RPMI 1640(含10%FBS)调整富集的单核细胞浓度至5×105 cells/mL,铺于24孔板上,同时加入重组人IL-4(500 U/ml)和GM-CSF(500 U/ml),37℃,5%CO2培养箱中孵育。
4. 48h后,培养板中培养基进行半量换液,同时补充重组人IL-4(500 U/ml)和GM-CSF(500 U/ml),继续刺激2天。
5. 第5天,收获未成熟的树突细胞,即单核细胞来源树突状细胞(monocyte-Derived dendritic cells, MoDCs),用于下游实验。吸取培养板中细胞转移至离心管,对细胞进行计数,并用细胞活力染料和CD3(T细胞marker), CD14(单核细胞 marker)和CD209(MoDCs marker)的抗体对获得的MoDCs样品进行染色,检测其活性及分化情况。
6. 成熟DCs激活:为获得完全成熟的DCs,通常可使用LPS或TNF-alpha/IL-6/IL-1β/PGE2进一步刺激上述细胞,具体方案:用LPS(0.5 μg/ml)或 TNF-alpha(10ng/ml)、IL-6(10ng/ml)、IL-1β(10ng/ml)、PGE2(1μmol/l)刺激24-48h。之后可使用流式细胞术(CD80、CD86)检测DCs成熟情况。
二、从人脐带血CD34+造血前体细胞诱导DCs
1. 获得新鲜脐带血,无菌条件下通过Ficoll-Hypaque梯度离心获得脐血单核细胞(CBMCs)。
(CBMCs可用7.5%DMSO,50%FBS冻存,用于后续实验。复苏时,37℃快速解冻,加入DNase I的培养基,室温离心15min。)
2. CD34+造血前体细胞获得及培养:使用商业化磁珠分选试剂盒如 EasySep™ Human CD34 Positive selection kit分选获得CD34+前体细胞。CD34+前体细胞用RPMI 1640 培养基(含10% FBS, 2 mM L-glutamine, 5×10-5 M 2-mercaptoethanol, penicillin (100 U/ml) 及streptomycin(100 ng/ml))调整细胞浓度至1×105 cells/mL,铺于24孔板上,并加入重组人GM-CSF(20 ng/ml)、IL-4(20 ng/ml),、TNF-α(20 ng/ml)、SCF(100 ng/ml)、Flt3 ligand(100ng/ml)或GM-CSF(20 ng/ml)、TNF-α(20 ng/ml),37℃,5% CO2培养箱中培养,每周2次采用半量换液,补加新鲜培养基及细胞因子,持续培养14天。
3. 14天后,收获未成熟树突细胞,即脐血来源树突状细胞(cord blood mononuclear cells,CBDCs)。吸取培养板中细胞,转移至离心管,对细胞进行计数,并用细胞活力染料和CD1a、CD14、CD33、CD34抗体对获得的CBDCs细胞样品进行染色,检测其活性及分化情况。
4. 成熟DCs激活:为获得完全成熟的DCs,通常可使用PolyI:C或LPS进一步刺激上述细胞,具体方案:用PolyI:C(10 μg/ml)或LPS(100–500 ng/ml)刺激24h。之后可使用流式细胞术(CD1a、CD14、 CD33、 CD34、HLADR、CD40、 CD80、CD86)检测DCs成熟情况。
*以上方案供参考,根据实验情况进行适当调整优化。
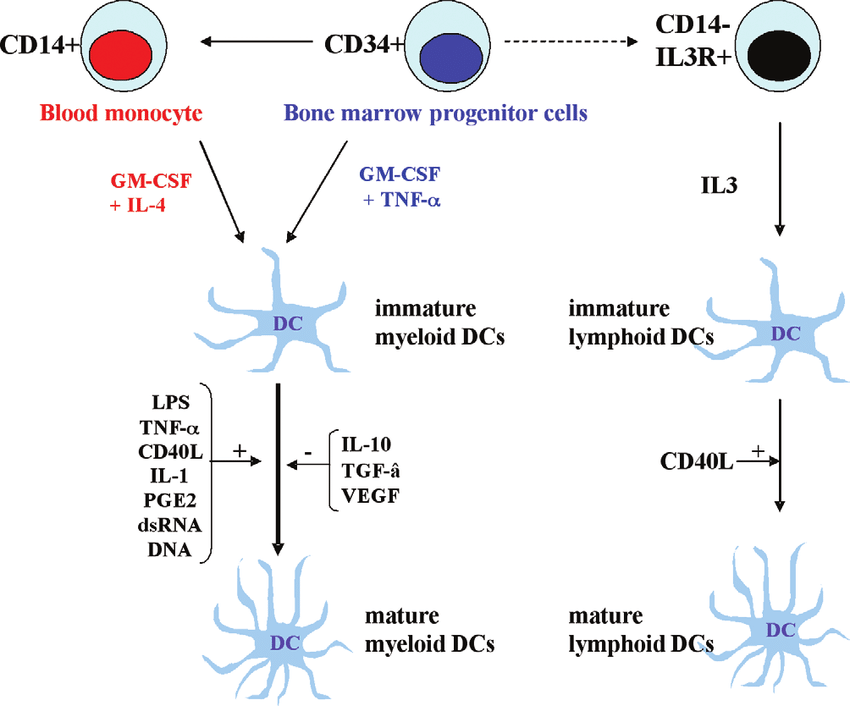
Fig. DC life cycle. Immature myeloid DCs can differentiate from CD34 + stem cells cultured with GM-CSF and TNF-α, or CD14 + monocytes cultured by GM-CSF and IL-4.(From Histol Histopathol. 2004 Jan;19(1):317-24.)
产品推荐:
文献引用:
· Thaize Quiroga Chometon et al. A protocol for rapid monocyte isolation and generation of singular human monocytederived dendritic cells.PLoS One. 2020 Apr 9;15(4):e0231132.
· Nicole Bedke et al. A method for the generation of large numbers of dendritic cells from CD34+ hematopoietic stem cells from cord blood. J Immunol Methods. 2020 Feb;477:112703.
· Miodrag Colić et al. Comparison of two different protocols for the induction of maturation of human dendritic cells in vitro.Vojnosanit Pregl. 2004 Sep-Oct;61(5):471-8.
· Marcia F Mata et al. A modified CD34+ hematopoietic stem and progenitor cell isolation strategy from cryopreserved human umbilical cord blood.Transfusion. 2019 Dec;59(12):3560-3569.
· C Caux et al. CD34+ hematopoietic progenitors from human cord blood differentiate along two independent dendritic cell pathways in response to GM-CSF+TNF alpha.J Exp Med. 1996 Aug 1;184(2):695-706.
· Wilfried Posch et al. Generation of Human Monocyte-derived Dendritic Cells from Whole Blood.J Vis Exp. 2016 Dec 24;(118):54968.
· Jitka Fučíková et al. Poly I: C-activated dendritic cells that were generated in CellGro for use in cancer immunotherapy trials. J Transl Med. 2011 Dec 30;9:223.


